Step-up bonds are special types of bonds that offer a lower interest rate at the beginning with a provision for an interest rate increase after a certain period. The number and level of the rate increase, as well as the timing, depends on the bond terms. The step-up bonds may have a single interest rate rise or multiple interest rate rises.
However, the increases of the bond’s coupon rates and their step-up dates are predefined by the issuer at the start. Some step-up bonds allow for an adjustment of the interest rate to the inflation rate. It means the bond interest rate would increase with inflation and decrease with deflation.
A strong example of such bonds is Treasury Inflation-Protected Securities (TIPS) that protect the investment value against inflation. TIPSs make coupon payments twice a year at a fixed rate but this rate is applied to the adjusted principal The principal of a TIPS rises with inflation and diminishes with deflation following the Consumer Price Index assessment. When a TIPS matures, the adjusted principal or original principal is paid to an investor.
As with any other type of bond, step-up bonds can also be callable. The call feature provides the bond issuer with protection against declining interest rates and is usually attached to the bond when the issuer anticipates the interest rates fall.
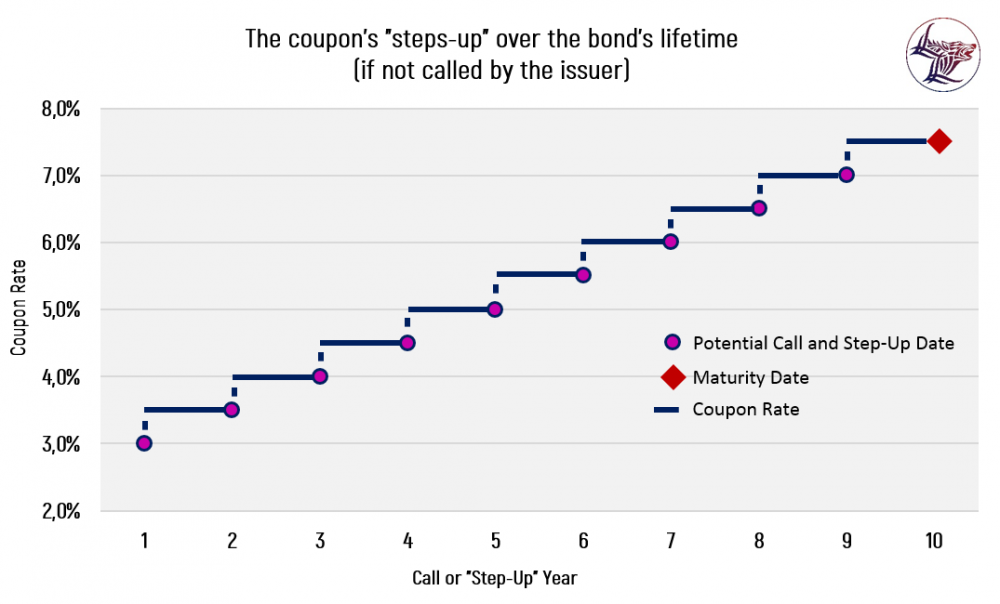
The attached image illustrates a situation where a step-up bond provides for an annual increase of coupon payments in the amount of 1% point after one year, and 0,5% points increase after each year onward over ten years of the bond lifetime. The bond can also be called after one year on the call or step-up date, and each year onward over the bond’s 10-year lifecycle. The call or step-up is announced on designated dates set by the bond’s terms. If the bond is called, the bondholder would receive the call price, which is usually the bond’s face value, plus the accrued interest to date.
Sometimes a call premium is also paid. Call provisions are more frequently used in corporate and municipal bonds.
Step-up bonds typically do better than other fixed-rate investments in a rising-rate environment, as they to a certain degree protect the bondholder from the risk of losing out on higher market rates. Step-up bonds prices are also less volatile. However, if market rate rises occur at a faster pace than the step-up increases, then the bondholder would not be secure from an interest rate risk.
Stay tuned with Wolfline Capital and you will learn more insightful things about capital markets and assets management.
